What is RFID (radio frequency identification)?
RFID stands for radio frequency identification. It's a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track RFID tags attached to objects.
What Is the Difference Between Passive RFID Tags and Active RFID Tags?
RFID tags can be passive RFID tags, meaning they don't have a power source and rely on the energy from the reader to transmit data, or active RFID tags, meaning they have their own power source (battery) and can actively transmit data. Passive RFID tags have a shorter read range than their active RFID counterparts. Passive RFID tags are also typically less expensive than active RFID tags and have a longer lifespan than active RFID tags due to not having a battery.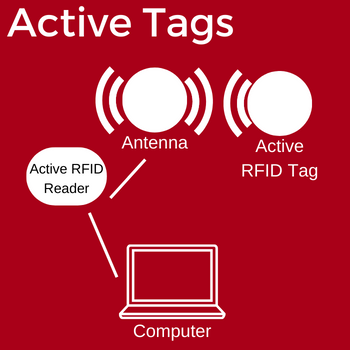
RFID technology is used in a wide range of applications, including fixed asset tracking, inventory management in retail, tracking goods in supply chains, access control in buildings and even contactless payment cards and toll booth passes.
What Is the Difference Between Low Frequency (LF) and High Frequency (HF) RFID Tags?
There are different frequencies at which RFID technology operates, which can affect the range and capabilities of the system. Low-frequency (LF) operates at 125-134 KHz and can be read up to 6 inches. Applications for low frequency include access control. High frequency (HF) operates at 13.56 MHz and can be read up to 1-2 feet from the reader. Applications for high frequency RFID include access control and NFC (Near Field Communication) for things like contactless payments.

What Are Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID Tags?
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) operates at 915-928 MHz and can be read over 20 ft. from the reader. Applications for UHF RFID tags include asset tracking, supply chain and logistics.
How Does RFID Work?
The RFID systems consist of a tag and a reader. The tag contains a microchip and an antenna. The microchip stores information about the item it's attached to. The RFID reader is a device that emits radio frequency signals. It generates an electromagnetic field that provides the energy for the RFID tag to operate. When the RFID tag comes into the range of the RFID reader's electromagnetic field it gets activated. If it's a passive RFID tag, it uses the energy from the reader's field to power up. The RFID reader sends out a signal that activates the tag. The RFID tag then transmits its stored information back to the RFID reader using radio waves. This information can include unique numbers or more detailed data about the object. The RFID reader captures the data transmitted by the RFID tag and sends it to a computer system for processing. This can be used for various applications such as asset tracking, inventory management, access control and more.
information about the item it's attached to. The RFID reader is a device that emits radio frequency signals. It generates an electromagnetic field that provides the energy for the RFID tag to operate. When the RFID tag comes into the range of the RFID reader's electromagnetic field it gets activated. If it's a passive RFID tag, it uses the energy from the reader's field to power up. The RFID reader sends out a signal that activates the tag. The RFID tag then transmits its stored information back to the RFID reader using radio waves. This information can include unique numbers or more detailed data about the object. The RFID reader captures the data transmitted by the RFID tag and sends it to a computer system for processing. This can be used for various applications such as asset tracking, inventory management, access control and more.
Overall, RFID technology is extremely versatile and plays a crucial role in many industries for tracking and managing assets efficiently.
For more information on what RFID technology is and how it works, please contact Metalcraft at 800-437-5283 or [email protected].
 | About the Author: Aaron HobertAaron Hobert is our RFID Technical Specialist. Hobert joined Metalcraft in September of 1994 as a Litho Press Operator, became the Autograph Team Lead in 1998 and in April 2005 he became the RFID Sales Support Rep. He was named our RFID Technical Specialist in 2008. Aaron lives outside Charles City with his wife Diane. Mobile Phone: 641-330-2660 Email: [email protected] Office: 3360 9th St. SW, Mason City, IA 50401 Office Phone: 641-423-9460 |




