RFID (radio frequency identification) inlays are essential components in RFID technology, used in various applications such as tracking inventory, managing supply chains, and contactless payments. Here's an overview of the RFID inlay manufacturing process.
Design and Planning
The process typically begins with the design phase, where engineers create the layout of the RFID inlay. This involves determining the placement and configuration of the antenna, as well as the chip that will be integrated into the inlay.
Antenna Production
Antenna production plays a pivotal role in the RFID inlay manufacturing process, serving as the foundation for effective
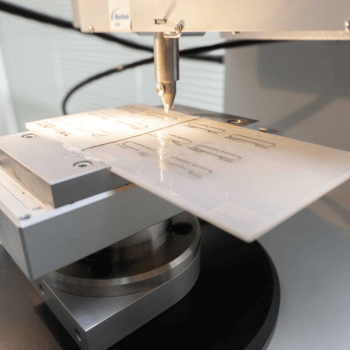
communication and data transfer in RFID systems. The design and fabrication of antennas require precision and expertise to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with various applications. Techniques such as printing, etching, or lithography are employed to create intricate antenna patters on flexible substrates. These antennas are crucial components that interact with RFID readers to transmit and receive data wirelessly. The quality and efficiency of antenna production directly impact the overall performance and reliability of RFID inlays, influencing factors such as read range, data transmission speed, and resistance to environmental conditions. Therefore, meticulous attention to detail in antenna production is essential to meet the diverse needs of RFID applications across industries ranging from retail and logistics to healthcare and manufacturing.
Chip Attachment
Once the antenna is produced, the next step is to attach the RFID chip. This chip contains the electronic components necessary for communication and data storage. The chip is typically attached to the antenna using a method such as flip-chip bonding, where solder bumps on the chip are aligned with corresponding pads on the antenna and then bonded using heat and pressure.
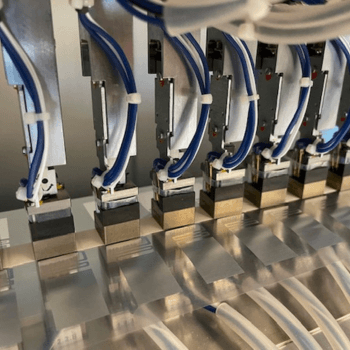
This phase plays a pivotal role in determining the overall performance and reliability of the RFID inlay, facilitating seamless communication between the chip and the reader, thus enabling efficient tracking and identification in various applications, from supply chain management to asset tracking.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation is a pivotal stage in the RFID inlay manufacturing process, ensuring the protection and longevity of the delicate electronic components housed within the inlay. During encapsulation, the inlay assembly, comprising the chip and antenna, is encased in a protective material, typically a durable polymer such as polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This encapsulation shields the electronic elements from environmental factors like moisture, temperature variations, and physical damage, safeguarding their functionality in challenging operational conditions. Moreover, encapsulation enhances the mechanical stability of the inlay, facilitating smooth integration into various RFID applications, from product authentication to inventory management, while maintaining consistent performance and reliability over time.
Testing and Quality Control
After encapsulation, the RFID inlays undergo rigorous testing to ensure that they meet the required performance standards. Testing and quality control are integral aspects of the RFID inlay manufacturing process, ensuring the reliability and functionality of the final product. Rigorous testing protocols are implemented at various stages, encompassing the examination of materials, fabrication processes, and finished inlays. These tests encompass parameters such as chip functionality, antenna performance, reading range, and durability. Advanced testing equipment and methodologies, including impedance analyzers and RF chambers, are employed to verify compliance with industry standards and customer requirements. Additionally, quality control measures such as visual inspection and sample testing are executed to detect any defects or irregularities, guaranteeing that only high-quality RFID inlays are delivered to customers, ready for seamless integration into diverse applications ranging from inventory management to access control systems.
Testing and quality control are integral aspects of the RFID inlay manufacturing process, ensuring the reliability and functionality of the final product. Rigorous testing protocols are implemented at various stages, encompassing the examination of materials, fabrication processes, and finished inlays. These tests encompass parameters such as chip functionality, antenna performance, reading range, and durability. Advanced testing equipment and methodologies, including impedance analyzers and RF chambers, are employed to verify compliance with industry standards and customer requirements. Additionally, quality control measures such as visual inspection and sample testing are executed to detect any defects or irregularities, guaranteeing that only high-quality RFID inlays are delivered to customers, ready for seamless integration into diverse applications ranging from inventory management to access control systems.
Finalization and Packaging
Once the RFID inlays pass quality control, they are finalized by trimming excess material and preparing them for distribution. Inlays may be supplied in rolls, sheets, or individual units, depending on the specific requirements of the customer and the intended application. Packaging may include additional protective measures such as anti-static packaging or moisture barriers to further safeguard the inlays during transportation and storage.
Integration into End Products
Finally, the RFID inlays are integrated into end products such as smart cards, labels, tags, or other items, depending on their intended use. This integration may involve processes such as lamination (for smart cards), adhesive application (for labels), or embedding (for industrial applications).
Throughout the RFID inlay manufacturing process, attention to detail, precision, and quality control are essential to ensure the reliability and performance of RFID inlays in real-world applications.
Overcoming challenges in the RFID Inlay manufacturing process
Overcoming challenges in the RFID inlay manufacturing requires a multi-faceted approach that emphasizes innovation, process optimization, and quality management. Firstly, investing in research and development to enhance materials and production techniques can lead to more robust and cost-effective processes. Additionally, implementing stringent quality control measures throughout each stage of manufacturing helps identify and rectify issues early on. Collaboration with suppliers and partners can foster knowledge exchange and access to cutting-edge technologies. Moreover, maintaining flexibility in production lines allows for swift adjustments to accommodate changing market demands or unforeseen challenges. Lastly, fostering a culture of continuous improvement encourages teams to actively seek and implement solutions to address any obstacles encountered, ensuring the consistent delivery of high-quality RFID inlays.
 | About the Author: Marianne AlvaradoMarianne Alvarado is our Vice President of Sales. Alvarado joined Metalcraft in March of 2000 as a Territory Specialist, became Sales Manager in January 2022 and was named Vice President of Sales during August of 2023. She leads both the Outside and Inside Sales teams. Marianne lives in Davenport with her husband, Dave Beeman. Mobile Phone: 641-529-9492 Email: [email protected] Office: 3360 9th St. SW, Mason City, IA 50401 Office Phone: 641-423-9460 |